Archive for 2010
Geologist on “Gipskeuper” / Anhydrite – Stuttgart 21
via Amphibol
update Saturday; September 4, 2010 The paper “Nürnberger Nachrichten” published an article today pointing out the geological risks of Stuttgart 21.
Where is it?
What has happened to the oil in the gulf?
Has it disappeared? Is it still there? Lots of people, lots of thought. And those bacteria sure must have been hungry!
Identi.ca Weekly Updates for 2010-08-25
- my brain wanted to read #AGU10 RT @AutoCAD: register for #AU2010 early? free AU Membership today. http://bit.ly/crNSF9 (via @engis) #
- Jahrestreffen #Kontakt e.V. am 26. November! Are you there? https://www.xing.com/events/12-jahrestreffen-kontakt-551441 #
- Three Gorges Dam not as great as anticipated: http://ke-we.net/2ej #
- Forward #osmosis instead of backward – consumes less #energy New Scientist http://bit.ly/d8vdzc (via @columbiawater) #
Water Cycle Hip Hop
Jo! Listen to the “soundtrack of science”! Rain! Rain! (via WaterWired)
Estimate the Distribution of an Underlying Process Based on Samples
Say you have many sets of samples (measurements). What do you do if you wanted to estimate the distribution of the underlying population? Ok, if all your samples are well behaving, you throw them in one pot, and estimate the distribution based on all the samples. Ok.
Now, what if you wanted, for whatever reason, to estimate the underlying distribution based on the individual sets of your samples? What you could do is estimate a distribution based on each sample. Then you would have to somehow average the distributions. How would you do that? By multiplication? Turns out – no. In fact, the average of the density functions of each sample seems to be a pretty good estimator of the underlying density function.
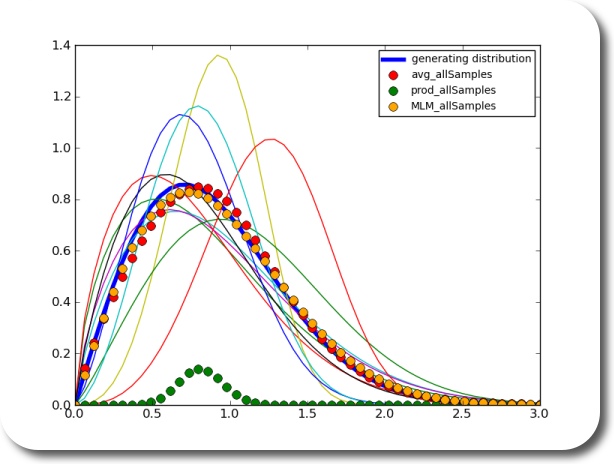
using 10 sets of samples with 10 samples each
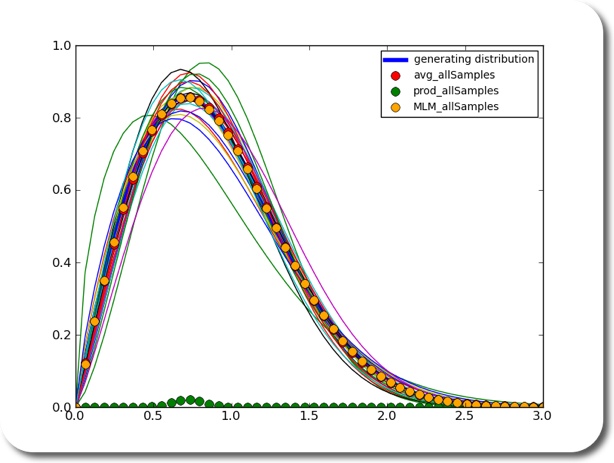
using 25 sets of samples with 100 samples each
Classic Books on Statistics and Hydrogeology – in German
The book-recommendations on this book are among the most popular posts on this blog:
- my list of rcommended hydrogeology books;
- individual book reviews of “bottled and sold”, “bottlemania” “numbers rule your world” or “just enough”;
These recommendations so far have all been for books written in english. They are not all purely technical books or particularly textbooks. However, they are all related to the theme of “water”, despite my hands-on quantitative-statistical take on that theme.
Two things happened in the recent past: I realized that I use wikipedia for surprisingly many tasks. I realized that I haven’t used a book in ages for example to look up a distribution function. The other thing that happened, just the other day, was that I took a fairly old programming book, because I wanted to re-read on a certain topic. And I knew it was covered in that (old) book well.
That’s when I thought, that I really like well written books, despite the wickedness of the internet (despite the fact that it recently was claimed to be dead – or not). Then I wondered, what are the best German written books related to the subject I am working in and which also is the topic of this blog? Of course, this is a tough question. And the two books I am going to name in a second are most likely not the only ones. However, they are the two that came to my mind immediately:
The statistics book appears a bit daunting at first with its 1145 pages. I don’t believe it is possible to read the entire book and neither it is recommended by the authors. However, it has happened to me many times that I was looking for a certain topic, like “How does the Wilcoxon Rank Test work?”, and sure enough I found theory for the test as well as an example in the book.
In contrast to statistics, hydrogeology is not as clearly defined. It’s much harder to distinguish a given topic to be or not to be “a hydrogeology topic”. Hence it would seem much harder to write a book on “hydrogeology”, because it would have to cover many topics. However, Hölting and Coldewey have done an excellent job to explain in short and precise language the basics of hydrogeology, from geology, well hydraulic to chemical aspects. It deserves special mentioning that there is a nice chapter on practical aspects, for example on how to get water out of the ground or groundwater protection.
Identi.ca Weekly Updates for 2010-08-18
- RT @drjerque: Wow. Frazil ice video…every geo / hydro must see: http://bit.ly/brS1ar (via @cbdawson) #
- #kesselfieber -neue Seite über things to do in #stuttgart http://kesselfieber.de/ @kesselfieber #
- @BoreholeGroup Ah, drilling! 🙂 Nice pics! But I thought you were drilling from ships? in reply to BoreholeGroup #
- Twitter for #science awesome new ideas via post on complexity of sinuous #channel #deposits in 3D http://bit.ly/bjcfEn (via @highlyanne) #
- #IEEE special issue on #water and #energy http://ke-we.net/29o #
- Need a #laptop (MacBookPro)? I'm selling one on eBay.de: http://ke-we.net/28r#ht_2501wt_1139 #
Identi.ca Weekly Updates for 2010-08-04
- RT @EagerEyes: Lightning filmed at 9,000 fps. http://youtu.be/-bvmEYxEYiA (via @theAGU) #
- #mathematica example notebook on #statistics and #weather Nice! http://blog.wolfram.com/2010/07/29/is-the-weather-biased/ #
Floods in Pakistan
Various newsoutlets report on floods in Pakistan (NYT 1, NYT2, globeandmail. About 800 people or more reportedly died. From a european perspective that seems quite a lot.
Nobody writes about why so many people died, or what the causes were: are there reservoirs? What was the estimated return period?
update Wednesday; August 4, 2010: There are reports that in Pakistan’s northwest, precipitation intensities were as high as 312mm within 36 hours.
update Saturday; August 14, 2010 NPR titles: “China, Pakistan Floods: Preventable Disasters?”
update Sunday; August 15, 2010 The Google Earth Blog has satellite images to be looked at in Google Earth showing the extent of the flood in Pakistan
update Tuesday; August 17, 2010:
- Steven Solomon’s view as written in the NY Times. He points out that the crazy thing is that Pakistan actually has a fresh water shortage.
- here’s a pretty impressive image from NASA (link to article; via Anne Jefferson @highlyanne )

Extent of flood in Pakistan on August 17, 2010
update Friday; August 20, 2010:
Over at howbigreally.com, there is an awesome tool where you can center the overlay of the current extent of the floods in Pakistan over any other area in the world.
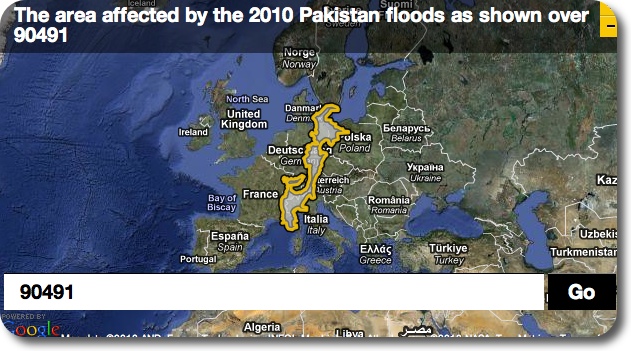
Extent of current pakistan flood over central Europe
The CBC has a new article, stating that 4 million people are left homeless
updata Friday; November 19, 2010 … and Clinton says it’s climate change! Other people disagree Also the longer-term consequences are starting to emerge. I think especially worrisome is the question of what might happen to the food-situation next year?
Bottled and Sold
Peter H. Gleich sets the theme for his book “Bottled and Sold: The Story Behind Our Obsession with Bottled Water” nicely at the very beginning
Think about where you are right now. How far away is the nearest faucet with safe water? Probably not very far. Yet every second of every day in the United States, a thousand plastic bottles are thrown away. Eighty-five million bottles a day. More than thirty billion bottles a year at a cost to consumers of tens of billions of dollars. And for every bottle consumed in the U.S., another four are consumed around the world
and at the end of his book:
“I’ve decided to write this book in part to gain a better understanding of what the explosive growth of the bottled water industry really means for us and for the future of drinking water.”
This is only about one bottle every three days for every US citizen. When you look at it that way it’s not too much, but still these numbers highlight how much recycling-material (“waste”) is produced by the many people living on this planet.

Cover of Bottled and Sold
Europe vs. North America
As I currently live in Germany, I have to point out at the beginning, that the story of bottled water is slightly different here than in North America. Bottled water traditionally used to be “mineral water” and it existed for as long as I can remember. Traditionally it is being sold in heavy plastic crates with glass bottles for which you paid about 3 Euros extra as deposit. When I was a kid, I drank lots of water from faucets, but also lots of mineral water out of those bottles. Gleick mentions this difference between North America and Europe in his book. And I agree, it does exist, even though over the last few years I also do see a trend towards use of more bottled water and less tap water. Similar discussions have been going on on this blog before.
There is a list of the contents, at least the mineral content (ions), on every bottle of water sold in Germany, and there are some waters with high mineral content, and maybe those have some health benefit to them. At least, I agree with Gleick, it’s good for the consumer to know what’s inside the product that he buys, and if it’s “only” water. There does seem to be a slight movement recognizable, also in Europe, that goes away from bottled water and back to tap water. More and more people, also in Europe, bring their own bottle and fill it with tap water.
However, a common thing between the continents is the increasing force with which companies invade public spaces. Gleick gives a nice example of stadium of University of Central Florida (UCF Knights) where “a $54 million stadium had been built without a single drinking water fountain. And for ‘security’ reasons, no one could bring water into the stadium. The only water available for overheated fans was $3 bottled water from the concessionaires or water from the bathroom taps, and long before the end of the game, the concessionaires had run out of bottled water.”. I’ve been hearing stories that there are universities in Europe, where students and employees are no longer allowed to bring their own coffee powder and brew their own coffee, but they have to buy their coffee from the shops at the university.
Summary
“Bottled and Sold” gives a very structured view of the entire bottled water business. Gleick deals not only with the hydrogeology, geology, hydrology, sanitary engineering aspects, but also advertisement, business aspects, or religious aspects. As a comparison, “Bottlemania” is a detailed case study, where local people get problems with water extraction of a private company.
Inherently, there are so many stories in this book which cannot be retold here — how ancient cultures were proud to supply high quality drinking water for free to the public, how advertisement and through other means somehow society got scared of drinking tap water, how insanely huge and water consuming “state of the art” bottling plants are and how significant their impacts are on the local water systems where they are located at. You have to read the whole thing. And I do recommend to read the whole thing for everybody who works in any subject related to water, as well as for anybody who is concerned about water — and everybody should be concerned. I want to point out three examples
The first one is a piece of legislature, today it could be called “consumer protection legislature” that was passed in 1875 by the Massachusetts legislature — ‘an Act against selling unwholesome provisions’. How much weaker is current comparable legislature? Here is a quote of it:
“Whereas some evilly disposed persons, from motives of avarice and filthy lucre, have been induced to sell diseased, corrupted, contagious or unwholesome provisions, to the great nuisance of public health and peace: Be it therefore enacted by the Senate and House of Representatives… That if any person shall sell any such diseased, corrupted, contagious or unwholesome provisions, whether for meat or drink, knowing the same without making it known to the buyer… he shall be punished by fine, imprisonment, standing in the pillory, and binding to the good behaviour, or one or more of these punishments, to be inflicted according to the degree and aggravation of the offence.
One chapter’s topic is “If it’s called “Arctic Spring,” Why is it from Florida?”. This chapter sheds some light into the wild world of brand names, and current legislature on what kind of water must be called what names.
Gleick finishes his book with a “call to arms”, pointing out that
we are at a cross-road: either abandon our efforts to provide save public tap water for all in favor of privately produced and sold bottled water — or instead follow a soft path for water, a comprehensive approach to sustainable water management and use, requiring equitable access to water, proper application and use of economics, comprehensive protection of aquatic ecosystems, incentives for efficient water use, new sources of supply, smart use of innovative technology, improved water quality and delivery reliability, strong public participation in decision-making, and more.
update Monday; August 16, 2010: here’s a review at “Water Link International“